Environmental economic sector / Green Jobs
Green jobs are jobs in the environmental economy. The environmental-economic accounts provide figures on environmentally-related production and employment as part of their monetary account ‘Environmental goods and services sector (EGSS)’. In this concept, harmonized at European level, an internationally comparable definition for activities that can be described as green jobs has been drawn up. It includes jobs to measure, prevent, limit, minimise and correct environmental damage and manage natural resources both in the production of goods and technologies and in the service sector. These include organic farmers, solar technicians, manufacturers of passive houses, environmental consultants and much more.

In 2019, the European Commission adopted the Green Deal - an ambitious roadmap for a sustainable, resource-efficient and competitive economy. The European Union should become climate neutral by 2050. The green transformation envisaged by the Green Deal means that more labour will be needed in the environmental economy in the future - especially in the areas of renewable energy, construction and agriculture.
Green jobs and turnover in the environmental economic sector
“Green jobs” have been developing positively for a longer time in Austria. In 2008, around 175,200 employees worked in the environmental industry. This value increased to 204,500 by 2021. Measured in full-time equivalents, the number of employees in 2021 was around 193,400.
Including employees in public transport, there were around 235,000 environmental employees in Austria in 2021. Public transport is not part of the Environmental goods and services sector definition, but is included as additional information due to information demand at national level. Public transport includes passenger and freight transport on rail transport and the relevant shares of other passenger transport on land transport.
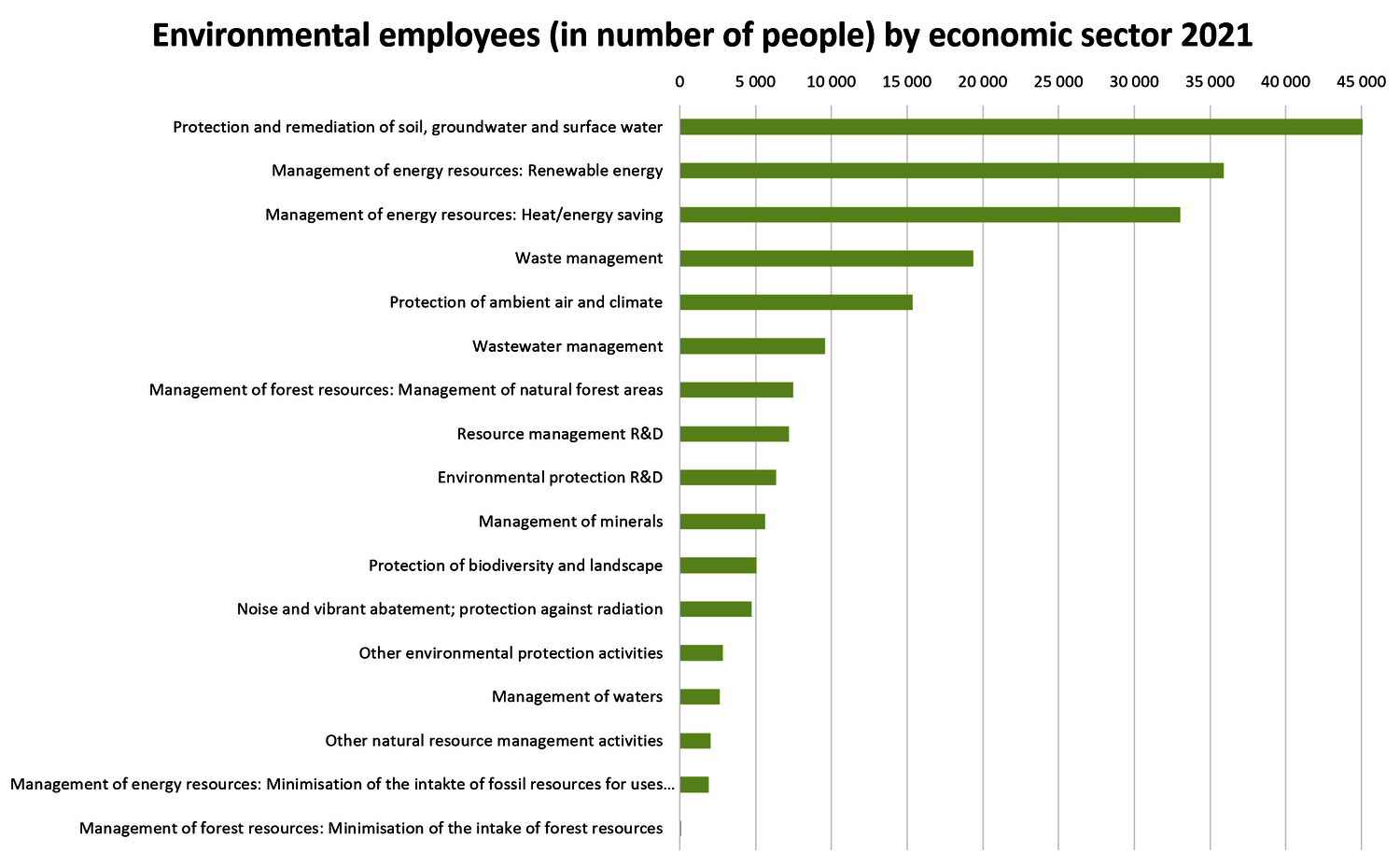
The most important environmental domain, ‘management of energy resources’ mainly consists of activities in the subdomains 'renewable energy' and 'heat/energy saving and management' and employed around 70,400 people in 2021 (34.4% of environmental employees). The environmental domain of ‘protection and remediation of soil, groundwater and surface water’ includes products from organic farming as environmental goods and employed 45,200 people in 2021. With 22.1% of environmental employees – compared to 7.9% of production value – this area is very employment-intensive. The classic environmental protection activities of ‘air pollution control and climate protection’ as well as ‘waste management’ also generated significant employment.
Development of the environmental economy
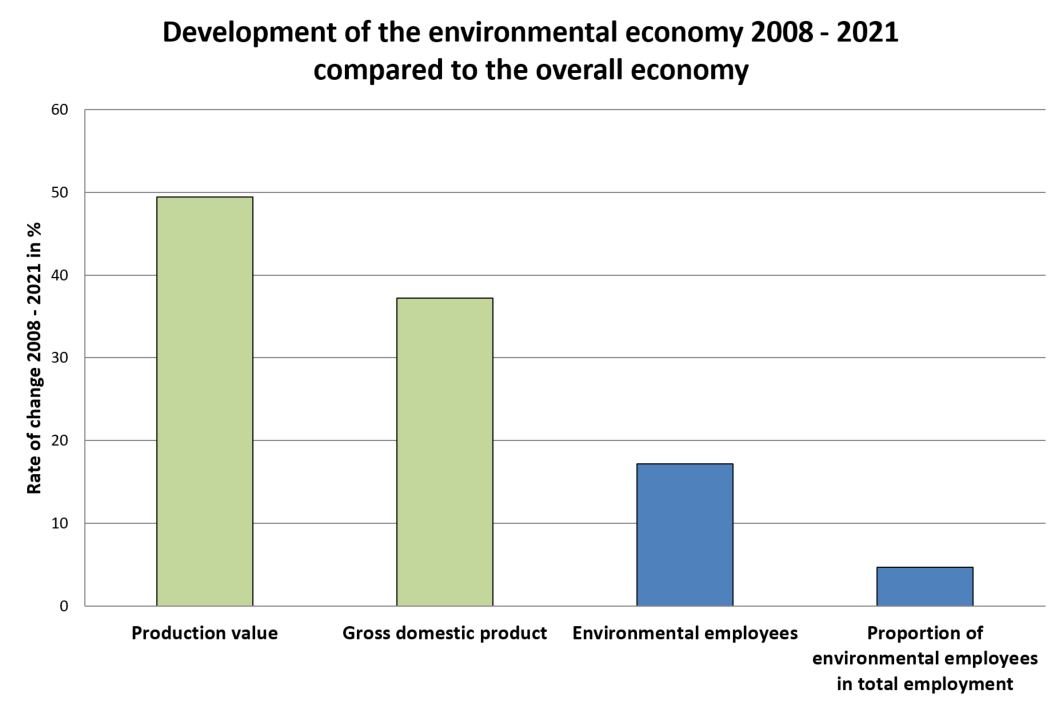
A comparison between the economic development of the environmental economy and the economy as a whole from 2008 to 2021 shows that the production value of the environmental economy increased more than the gross domestic product.
While the production value of the environmental economy increased by almost 50 % in this period, the gross domestic product recorded an increase of around 37% in the same time.
The number of environmental employees increased by over 17 % from 2008 to 2021, and the share of environmental employees in the total employment in Austria increased by around 4.6 % over these years.